Cash-Out Refinance vs. Home Equity Line of Credit: Choosing The Right One

Are you looking for a way to access equity in your home? If so, you may be considering a Cash-Out Refinance or a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC). Both options have their own pros and cons, so it's important to understand the differences between them before making a decision. This article will provide you with the information you need to know about Cash-Out Refinances and HELOCs, so you can decide which option may be right for your needs.
What is a Cash-Out Refinance?
A Cash-Out Refinance is a type of mortgage refinancing that allows homeowners to borrow against the equity they have built up in their properties. Homeowners can access this built-up equity by taking out a new loan for an amount greater than their existing mortgage balance. The difference between the new loan amount and the previous mortgage balance is then given to the borrower as cash. This cash can be used for various purposes, including debt consolidation, home renovations, educational expenses, or any other personal financial needs.
Eligibility Requirements and Steps of a Cash-Out Refinance
To obtain a Cash-Out Refinance, homeowners must meet certain eligibility criteria. Requirements include:
- Having enough equity in their homes
- A good credit score
- Stable source of income.
The process typically involves:
- Submitting a loan application
- Providing financial documentation
- Undergoing a home appraisal
If approved, the new loan replaces the existing mortgage, and the borrower receives the cash proceeds minus any associated fees and closing costs.
Unlock Financial Benefits with a Cash-Out Refinance
There are several benefits to using a Cash-Out Refinance. They include:
- Access to a lump sum of money without having to sell your home
- The interest rates on a Cash-Out Refinance are often lower compared to other forms of borrowing, such as personal loans or credit cards.
What is a HELOC?
A HELOC is an innovative financing solution that unlocks the potential of homeowners' accumulated home equity. Unlike a traditional Cash-Out Refinance, which replaces the existing mortgage with a new one, a HELOC operates as a flexible credit line, mirroring the functionality of a credit card. Homeowners are able to access funds up to a predetermined credit limit.
The Versatile Financial Tool for Home Renovations, Debt Consolidation, and More
This adaptability makes a HELOC well-suited for a wide range of financial endeavors, including:
- Home renovations
- Debt consolidation
- Educational expenses
- Other substantial purchases
- Backup source of emergency funds
Obtaining a HELOC requires meeting specific eligibility criteria established by lending institutions. Typically, homeowners must demonstrate:
- Enough equity in their properties
- A favorable credit score
- A steady source of income
The application process involves:
- Submitting financial documentation
- Undergoing a thorough credit check
- Arranging for a professional appraisal of the property to accurately determine the available equity
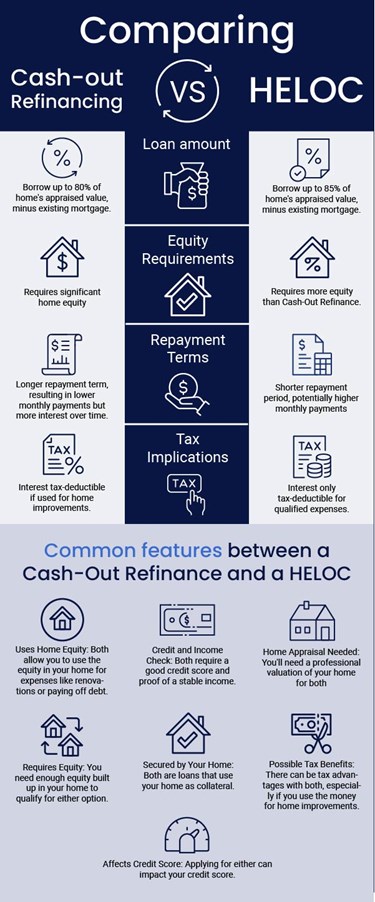
Comparing a Cash-Out Refinance and a HELOC
Comparing a Cash-Out Refinance and a HELOC and understanding their key differences and similarities can help you decide which one might be right for you.
Repayment Terms and Periods
A Cash-Out Refinance typically has a longer repayment term than a HELOC. This means you have more time to repay the loan, resulting in lower monthly payments. However, keep in mind that a longer repayment period also means you'll pay more interest over time. A HELOC, on the other hand, often comes with a shorter repayment period, usually ranging from 10-20 years. This can be beneficial if you want to pay off the debt quickly, but it can also result in higher monthly payments.
Loan Amounts and Equity Requirements
A Cash-Out Refinance allows you to borrow up to 80% of your home's appraised value, minus your existing mortgage balance. This can provide you with a substantial amount of cash, but it also means you need to have significant equity in your home. A HELOC, on the other hand, typically allows you to borrow up to 85% of your home's appraised value, minus your existing mortgage balance. This means you may be able to access more cash with a HELOC, but you'll need to have even more equity in your home.
Tax Implications
Cash-Out Refinances and HELOCs can have different tax implications. The interest paid on a Cash-Out Refinance is generally tax-deductible if the loan proceeds are used for home improvements. However, the interest paid on a HELOC is only tax-deductible if the loan proceeds are used for qualified expenses.
Should I Cash-Out Refinance or Get A HELOC? Pros and Cons
When considering whether to Cash-Out Refinance or obtain a HELOC, it is essential to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each option.
Pros of a Cash-Out Refinance:
- Longer repayment terms: Cash-Out Refinances usually have longer repayment periods, such as 15 or 30 years. This can reduce monthly payments.
- Option for a fixed interest rate: A Cash-Out Refinance may offer you a more dependable interest rate if you refinance from an Adjustable-Rate mortgage to a Fixed-Rate loan.
- Tax benefits: The interest paid on a Cash-Out Refinance may be tax-deductible, reducing your overall tax liability.
- Consolidates debt: A Cash-Out Refinance can combine high-interest debts, like credit card balances, into a single loan with a potentially lower interest rate.
Cons of a Cash-Out Refinance:
- Closing costs: Cash-Out Refinances include closing costs, like appraisal fees, title insurance, and lender fees. These can offset some refinancing benefits.
- Potential impact on credit score: Refinancing your mortgage can temporarily lower your credit score due to the hard credit inquiry involved in the process.
Pros of a HELOC:
- Flexibility: HELOCs offer flexibility in accessing funds as needed, up to the approved credit limit. This can be beneficial for ongoing or unexpected expenses.
- Interest-only payments: During the draw period of a HELOC, you may only be required to make interest-only payments, reducing your monthly payments.
- No prepayment penalties: HELOCs typically do not have prepayment penalties, allowing you to pay off the balance in full at any time without incurring additional charges.
Cons of a HELOC:
- Variable interest rates: HELOCs have variable interest rates, which can increase costs in the long run.
- Risk of default: If you fail to make the required payments on your HELOC, the lender can foreclose on your home.
- Second Lien Position: HELOCs are usually secured in a second lien position, meaning that if you default on your mortgage, the HELOC lender may not be paid back in full.
Weigh Your Options: Comparing a Cash-Out Refinance vs. HELOC for Financial Success
Ultimately, the decision between a Cash-Out Refinance and a HELOC depends on your individual financial situation and goals. Consider factors such as interest rates, repayment terms, tax implications, and your need for flexibility in accessing funds. Consult with your Loan Officer to get answers to your questions and find out which one might be right for your needs.
Cash-Out Refinance and HELOC FAQ’s
Can I qualify for a HELOC if I already have a Cash-Out Refinance?
Yes, you can qualify for a HELOC even if you already have a Cash-Out Refinance, as long as you meet the lender's requirements.
What are the tax implications of a Cash-Out Refinance vs. a HELOC?
The tax implications of a Cash-Out Refinance and a HELOC may vary, so it's best to consult with a tax professional to understand the specific implications for your situation.
How long does it take to get funds from a Cash-Out Refinance vs. a HELOC?
The time it takes to get funds from a Cash-Out Refinance is typically longer than getting funds from a HELOC, as it involves a full loan application and approval process.
How do fluctuating market rates affect a Cash-Out Refinance and a HELOC?
Fluctuating market rates can affect both a Cash-Out Refinance and a HELOC, potentially impacting the interest rates and monthly payments for both options.
